Matter
Matter is a pure substance or a mixture of substances
A pure substance (element or compound) has a constant composition and constant properties through a sample and from sample to sample
Elements are composed of atoms of the same atomic number and cannot be broken down by chemical change
Mixtures
A mixture is the combination of any two substances and can be separated by physical means
Each component in a mixture retains its original properties (i.e.: ionic components stay ionic)
Proportions of components in a mixture can be varied (i.e. 2 mol of NaCl in H2O vs. 3 mol NaCl in H2O)
Mixture Terminology
| Term | Definition | Example |
| Element | a substance made up of only one type of atom
Note: this is on an atomic scale |
iron, copper, magnesium |
| Compound | a substance made up of two or more types of atoms
Note: this is on an atomic scale |
water, salt, sugar |
| Substance | any element or substance; scientific way of saying "stuff" or "material" | sodium chloride, oil, potassium |
| Solute | The material added into a solvent. Gets dissolved. | Sugar |
| Solvent | Dissolves the solute. | Water |
| Solution | The resulting mixture | Sugar water |
| Solubility | relates to how much solute can dissolve in a solvent at a specific temperature and pressure | 40 grams of NaCl can dissolve in 100 grams H2O at 90 oC |
| Homogeneous | Mixtures that are the same throughout | Tomato soup |
| Heterogeneous | Mixtures that are different throughout | Beef stew |
| Unsaturated | Solutions are not full. They can dissolve more solute. | Sugar disappears when added |
| Saturated | Solutions are full. They cannot dissolve more solute. | Sugar falls to the bottom when added |
| Supersaturated | Solutions have more solute dissolved than they should be able to. | Formation of rock candy |
| Miscible | They can add (mix) together. | Food coloring and water |
| Immiscible | They cannot add (mix) together. | Vegetable oil and water |
| Colloid | Mixture that is cloudy, but the particles stay in the mixture and do not settle. | Milk |
| Suspension | Has particles that fall out of the solution and need to be shaken to mix. | Orange juice with pulp |
Separation Techniques
| Separation Technique | Definition | Example | Diagram |
| Sieving | Technique used to separate solid particles of different sizes | Rock and sand mixture |
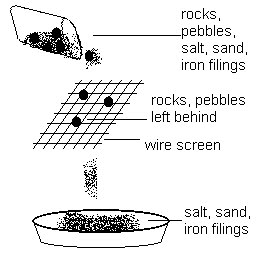
|
| Filtration | Technique used to separate an insoluble (substance that can’t dissolve) from a liquid | Sand and water mixture |
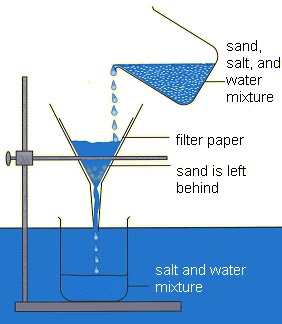
|
| Evaporation/ Boiling | Technique used to separate a soluble solid (substance that dissolves) from a liquid to obtain the solid | Salt water to obtain the salt |
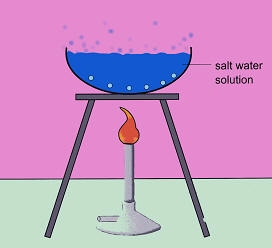
|
| Distillation | Technique used to separate a soluble solid and a liquid to obtain the liquid | Salt water to obtain the water |
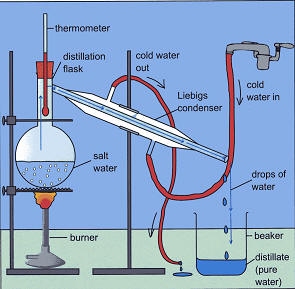
|
| Magnetism | Technique used to separate magnetic particles from a mixture | Iron particles and flour mixture |
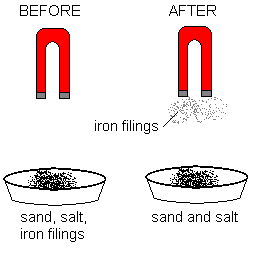
|
| Chromatography |
Separate particles by passing them through a medium (stationary phase) Particles travel at different rates through a solvent (mobile phase), separating them For gases or liquids |
Separating food coloring from a solution |
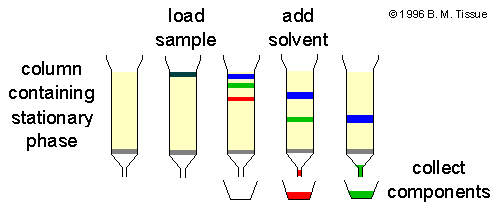
|