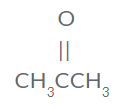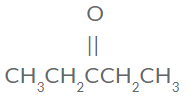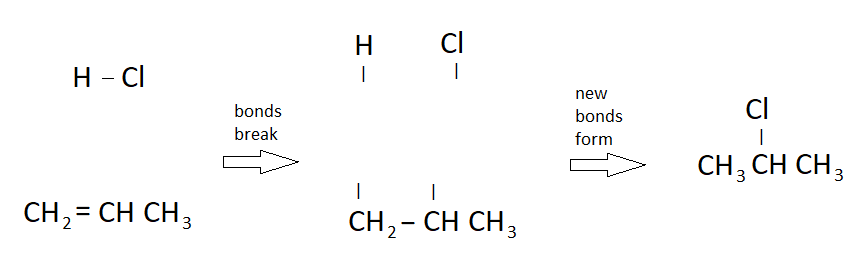Organic Chemistry
- Focuses on the elements: SPONCH
- sulfur, phosphorous, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen
- The main emphasis is on hydrocarbons
- carbon and hydrogen chains
- Organic compounds contain carbon atoms which can bond to one another in chains, rings, and networks

Saturated vs. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
- Saturated hydrocarbons contain only single bonds

- Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain at least one double or triple bond
- more than one pair of electrons is shared between two atoms
- these are alkenes or alkynes

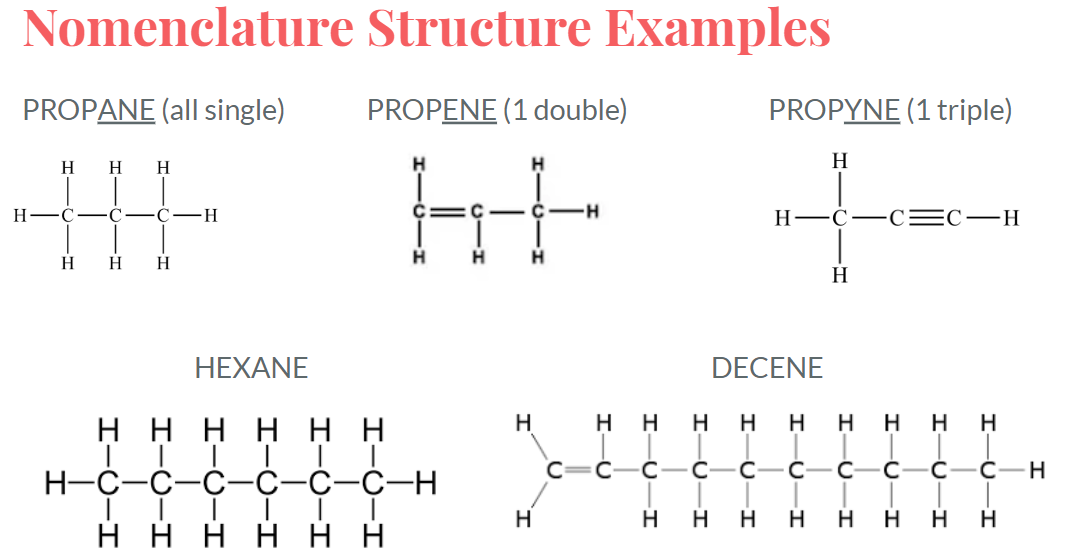
Nomenclature
- Nomenclature is the naming of structures
- Organic compounds can be named using the IUPAC system
- A prefix exists for the main chain that describes the number of carbons
- A suffix exists for the main chain that describes the type of bonding
- single, double, triple
- See Reference Table Q
- Numbers can be used to denote on which carbon a double bond (etc.) is located
- 1-butene has a double bond starting on carbon 1
- 2-butene has a double bond starting on carbon 2

Prefixes for Hydrocarbons (Table P)
Prefix |
Number of Carbons |
| meth- |
1 |
| eth- |
2 |
| prop- |
3 |
| but- |
4 |
| pent- |
5 |
| hex- |
6 |
| hept- |
7 |
| oct- |
8 |
| non- |
9 |
| dec- |
10 |
Suffixes for Hydrocarbons (Table Q)
Name |
Suffix |
Type of Bonding |
| alkane |
-ane |
all single |
| alkene |
-ene |
at least one double |
| alkyne |
-yne |
at least one triple |
Example: ethane → 2 carbons, all single bonds
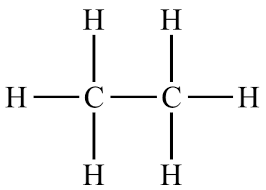
How Many Hydrogens?
- It would be a pain to draw the structures and count all the hydrogens
- There's an easier way, with a few basic formulas
- These are given to you in Reference Table Q
- If you know the number of carbons and the type of bonds, you can easily figure out the number of hydrogens
- You can also work backwards

Isomers
- Isomers are two (or more) versions of an organic compound that have the same molecular formula, but
different structures
- Example: butane: C4H10
- Note: the N- just means "normal" and doesn't need to be written

Functional Groups
- There are many types of organic compounds, not just hydrocarbons
- Each of these contains at least one functional group
- A functional group gives physical and chemical properties to a molecule
- Functional groups include:
- ketones
- aldehydes
- organic acids
- alcohols
- ethers
- esters
- halides
- amines
- amides
- amino acids
Comparing Ketones, Aldehydes, and Organic Acids

Comparing Alcohols, Ethers, and Esters

Functional Group Reference Table
- These are given on Reference Table R
- In the reference table, the functional group is shown, such as alcohol as -OH
- This means if you have a hydrocarbon with just an OH attached, you have an alcohol
- ethanol (ethyl alcohol) is CH3CH2OH
- In the "General Formula" column, you see R and R'
- These represent the rest of the molecule
- If the functional group includes C, you do count that carbon if you're naming the molecule
- The only functional group missing from the chart is amino acid
 |
Amino Acid
- This has an amine group -NH2
- and an acid group -COOH
- hence the name "amino acid"
|
|
 |
Classify the Compound Based on the Functional Group
| Compound |
Functional Group |
Type of Compound |
| CH3CH2OH |
-OH |
alcohol |
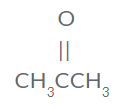 |
|
ketone |

|

|
organic acid |
| CH3CH2Br |
-Br |
halide |
| CH3CH2COOH |
-COOH |
organic acid |
Functional Group Drawing
- Draw the structure of butanic acid
- "but-" is the prefix for 4 carbons
- "-ic acid" means an organic acid with -COOH
- CH3CH2CH2COOH
- Draw the structure of 3-pentanone
- "pent-" is the prefix for 5 carbons
- "-one" means a ketone =C=O
- The "3-" means the functional group is on the third carbon
- CH3CH2CHOCH2CH3
- Or:
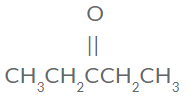
Organic Chemical Reactions
- There are several reaction types specific to organic chemistry
- addition
- substitution
- polymerization
- esterification
- fermentation
- saponification
- combustion
Organic Reaction: Addition
- When two molecules combine into a larger one
- requires an alkene or alkyne (alkanes won't work)
- this is like a synthesis chemical reaction
- Example:
- HCl and propene react to form 2-chloropropane:
- HCl + CH2=CHCH3 → CH3CHClCH3
- The double bond in propene breaks
- The bond in HCl breaks
- New bonds are formed between these molecules
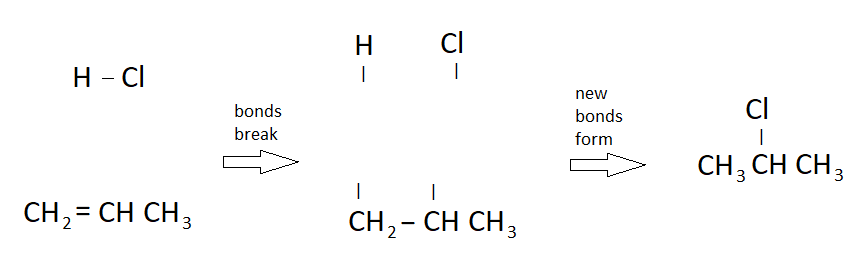
Organic Reaction: Substitution
- When two molecules swap a piece
- works with alkanes
- this is like a double displacement chemical reaction
- Example:
- HCl and 2-butanol react to form 2-chlorobutane and water:
- HCl + CH3CHOHCH2CH3 →
CH3CHClCH2CH3 + H2O
- The C-OH bond in 2-butanol breaks
- The bond in HCl breaks
- New bonds are formed by swapping partners (OH and Cl in this case)
- Two new molecules are made

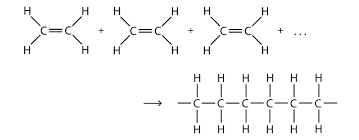
Organic Reaction: Polymerization
- This occurs when many smaller pieces (monomers) join together into one larger piece (polymer)
- This is the process behind making slime!
- The diagram shows molecules of ethene polymerizing into a long chain
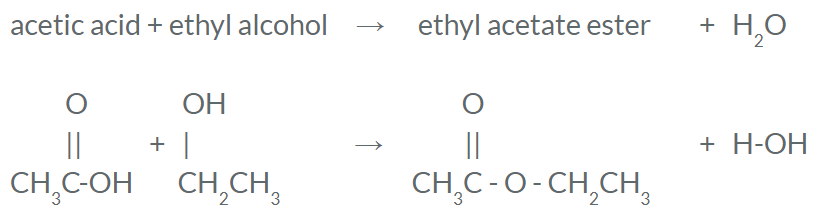
Organic Reaction: Esterification
- Esterification is the process of making an ester
- Esters produce fragrances and are used in perfume
- You can think of it like an "ester" egg has an odor
- Requires an organic acid and an alcohol
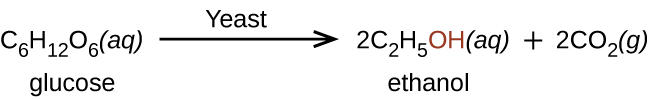
Organic Reaction: Fermentation
- Fermentation is the process of turning carbohydrates into an alcohol or an acid
- Yeast performs fermentation by converting sugar into alcohol
- Carbon dioxide is a byproduct
- Bacteria perform fermentation by converting carbohydrates into lactic acid
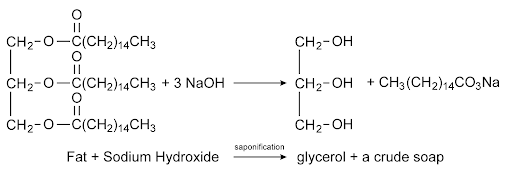
Organic Reaction: Saponification
- Saponification is the process of making soap
- In this, animal or vegetable fat is converted into soap in the presence of an alkali (like NaOH) and heat
- Soap works because it has a polar end (which links to water) and a nonpolar end (which links to oils)
Organic Reaction: Combustion
- Combustion is the process of burning oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water
- Combustion always involves molecular oxygen (O2)
- They are almost always exothermic, thus producing heat
- Focus on the basic reactants and products
hydrocarbon + O2 → CO2 + H2O
Combustion of propane:
C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O